The term PPC is an acronym that stands for pay-per-click. It is a type of search engine marketing (SEM) where advertisers bid for ad placement in search engines like Google, Bing, or Yahoo. Ads will appear alongside organic results at the top, bottom, and sometimes to the right of most SERPs (Search Engine Results Page). Every time an ad is clicked the advertiser is charged a fee based on real-time bidding as well as several other factors as determined by the search engine. The advantage to this type of advertising is that the advertiser is only charged when their ad is clicked regardless of the number of impressions (times seen by searchers).
Identifying a pay per click campaign can sometimes be tricky since most search engines offer pay-per-click ads in several forms and in some cases the ads are hard to spot.
If you search the web you’re bound to run into several types of paid advertising. The most popular type of PPC ad is the text ad. Other types of ads include: shopping, display, and local search.
Text Ads
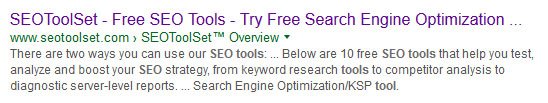
Google Adwords (Google’s PPC platform) offers 3-4 paid ads text ads at the top and bottom of their search results page. They are clearly marked with a green “ad” icon. See below. The advertiser with the highest ad rank (Bid + Quality Score) will win the top spot on the page every time the keywords they bid on are searched.

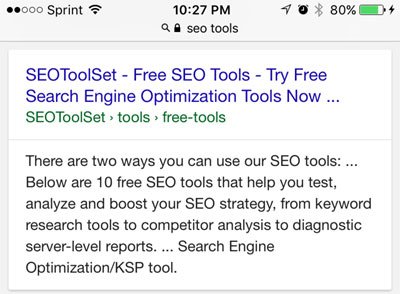
Bing Ads (Microsoft’s PPC platform) offers paid text ads at the top, bottom, and right side of the SERP. They are marked with an “ad” icon but it’s not as easy to spot. See below.

Shopping Ads
In addition to text ads, Google and Bing also offer PPC shopping ads. Shopping ads are not keyword based, but rather utilize a catalog of products with specific product groupings. The catalog is typically uploaded in CSV format with the advertisers latest products and pricing. Shopping ads let searchers see an image of the advertisers product, in addition to the title, current price, and short description.
Google displays their shopping ads at the top or right of a SERP. See below.

Bing Ads also offers a similar shopping experience. They also display their shopping ads at the top or right of a SERP. See below.

Display Ads
Google offers several forms of pay-per-click advertising. Google display ads give you the ability to showcase your ads (text or image ads) across their entire display network. According to Google, “this digital network spans over 2 million websites that reach over 90% of people online”. Their display network utilizes not only Google properties like YouTube and Gmail but a massive network of partner sites that earn revenue using the Adsense platform.
Ads in Google’s display network will typically showcase a blue AdChoices arrow in the top right corner of the ad.

There are several display ad sizes, the most popular are listed below.
- leaderboard (728×90)
- banner (468×60)
- skyscraper (120×600)
- wide skyscraper (160×600)
- small square (200×200)
- square (250×250)
- medium rectangle (300×250)
- large rectangle (336×280)
- half page (300×600)
- mobile banner (320×50)
- large leaderboard (970×90)
There are several ways to target your display ads. They can be keyword based or use interest targeting. You can also display ads to previous visitors to your site (AKA remarketing or retargeting).
Local Search Ads
Local search ads with Google can target specific locations and feature specific business locations. Just like Google’s other PPC ads, when people search for businesses near them via Google.com or Google Maps (Ex. plumber in Orlando, FL), they may see local search ads featuring business locations. Google’s local ads are displayed in purple.

Conclusion
Pay-per-click advertising has become the most popular type of digital advertising for one reason. It works. Here’s why.
- You only pay when someone is generally interested in your ad and clicks.
- You can get your ads up and running in minutes.
- With specific goals in place you can easily measure results.
- You can set a specific budget.
- And most importantly, it’s scalable. If a small campaign works and is driving revenue, there is a pretty good chance you’ll be able to increase your budget while maintaining the same percentage of success.